Towards Efficient Use of Multi-Scale Features in Transformer-Based Object Detectors
Multi-scale features have been proven highly effective for object detection but often come with huge and even prohibitive extra computation costs, especially for the recent Transformer-based detectors. In this paper, we propose Iterative Multi-scale Feature Aggregation (IMFA) – a generic paradigm that enables efficient use of multi-scale features in Transformer-based object detectors. The core idea is to exploit sparse multi-scale features from just a few crucial locations, and it is achieved with two novel designs. First, IMFA rearranges the Transformer encoderdecoder pipeline so that the encoded features can be iteratively updated based on the detection predictions. Second, IMFA sparsely samples scale-adaptive features for refined detection from just a few keypoint locations under the guidance of prior detection predictions. As a result, the sampled multi-scale features are sparse yet still highly beneficial for object detection. Extensive experiments show that the proposed IMFA boosts the performance of multiple Transformer-based object detectors significantly yet with only slight computational overhead.
Problem:: DETR의 Multi-Scale Feature 활용은 많은 연산량을 요구함
Solution:: Object Query에 Feature를 Aggregation하여 사용/Multi-Scale Feature를 전부 사용하지 않으므로 매번 업데이트
Novelty:: 기존 Stacked Encoder 구조를 벗어나 Stacked Encoder-Decoder 구조 제안/DETR에서 FPN을 대체할 수 있는 Multi Scale Feature 사용 방식에 대한 최초의 연구
Note:: 코드와 내용 모두 이해하기 쉬웠음. 저자들이 비슷한 연구로 QueryDET을 언급
Summary
Motivation
- Transformer 기반 Object Detector에서 Multi-Scale Feature를 활용하면 성능이 향상되나, 고해상도 특징 맵을 처리하는 Transformer의 Attention Mechanism이
의 높은 계산 복잡도를 가져 실용적이지 않음 - 특히 이미지 내 Background가 대부분이기 때문에 많은 연산이 낭비되는 문제 존재
- 기존의 Deformable DETR이나 Sparse DETR은 연산을 일부 줄였으나 여전히 특별한 Operator의 사용과 높은 메모리 요구량 등 한계 존재
Method
- Sparse한 Multi-Scale Feature를 효율적으로 사용하는 일반적인 Paradigm인 Iterative Multi-scale Feature Aggregation (IMFA) 제안
- 크게 두 가지 전략으로 구성:
- Iterative Update of Encoded Features:
- Sparse Multi-Scale Feature Sampling and Aggregation:
Iterative Update of Encoded Features
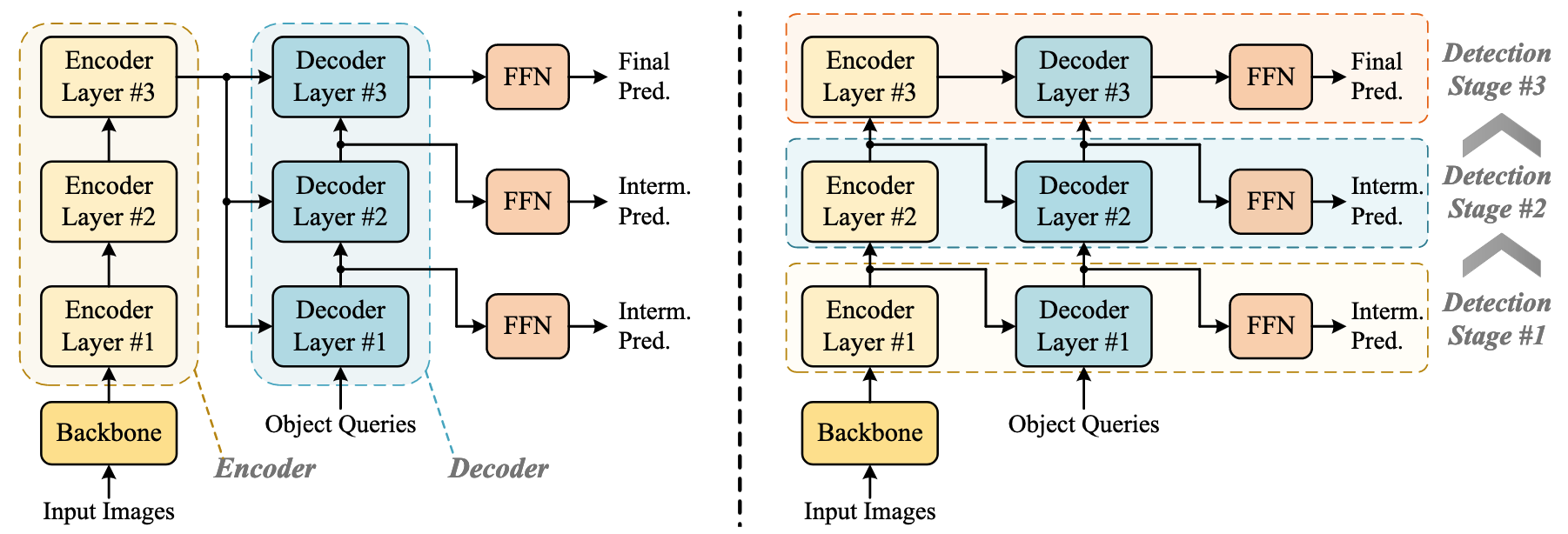
왼쪽: 기존 DETR 모델들, 오른쪽: 제안 방식
- 기존의 Encoder-Decoder 파이프라인을 재구성해 Encoder Layer와 Decoder Layer를 교차 배치, 매 단계에서 Encoded Features가 Detection 결과를 기반으로 반복 갱신되도록 설계
- 이를 통해 Detection Prediction 결과를 기반으로 Multi-Scale 특징을 효율적으로 활용 가능하게 함
Sparse Multi-Scale Feature Sampling and Aggregation
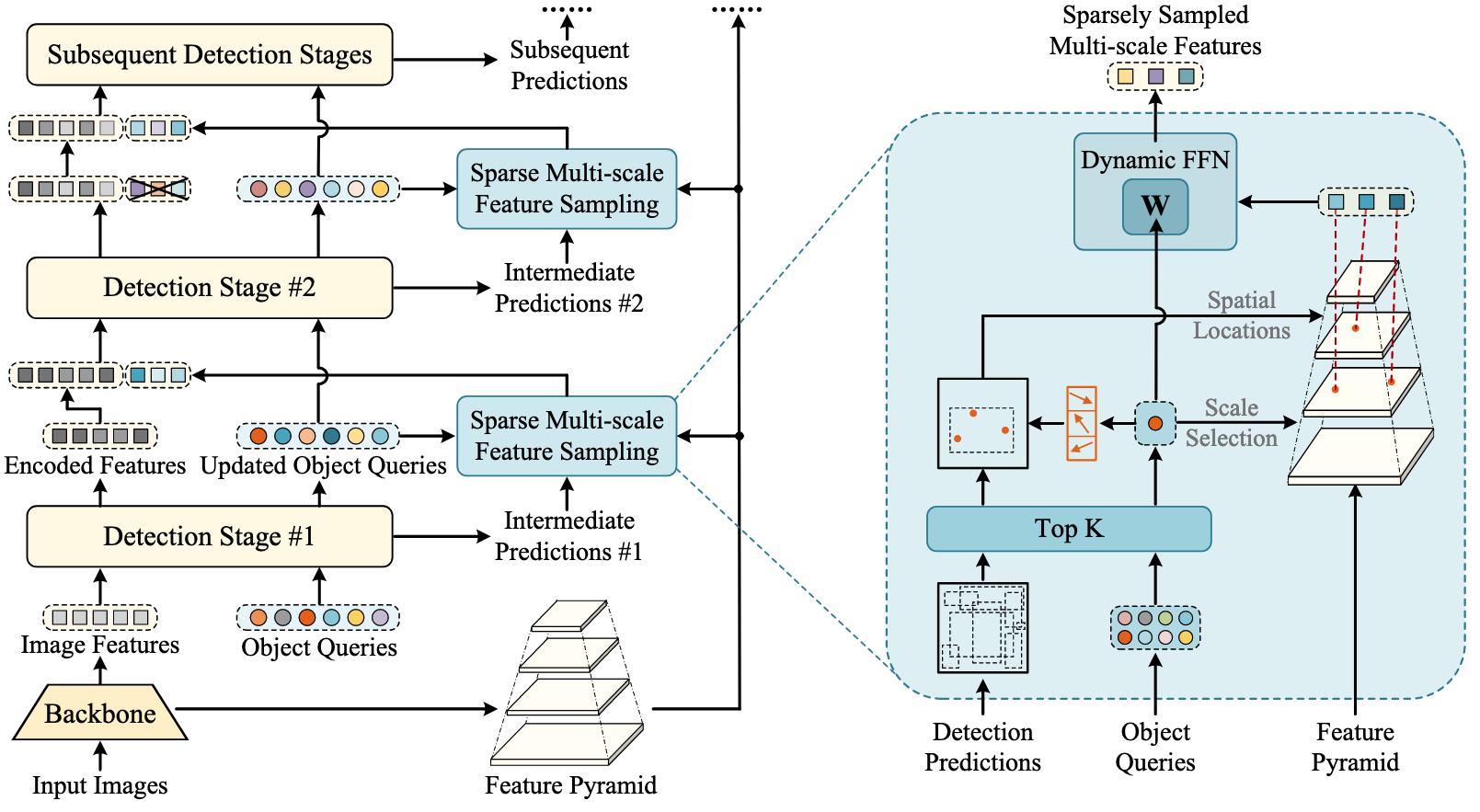
- 이전 Detection Prediction을 이용해 객체 존재 가능성이 높은 Promising Region만 선별적으로 선택
- 각 Region 내에서 소수의 대표적인 Keypoint를 찾고, 이 Keypoint에서만 Scale-Adaptive Multi-Scale Feature를 샘플링
-
전체 Object Query중 Top K 샘플링 (K는 전체 Object Query수의 10~50%)
-
Object Query마다 Sampling Location과 Scale Selection Weight를 예측
- Sampling Location은 해당 Query를 이용해 Decoder가 예측한 BBox 내부의 좌표 (Query당 8개 에측)
는 Query 의 좌표 에 해당하는 Feature - Scale Selection Weight
는 Feature맵의 레벨별로 얼마나 참조할지 결정
-
샘플링된 Sparse Features는 Dynamic Feed-Forward Network (Dynamic FFN)을 통해 Object Queries의 Semantic 정보를 통합하여 최종적인 특징 표현력을 향상
- Dynamic Weight는 Query마다 동적으로 FFN의 Weight를 생성하는 방식
-
Method 검증
- MS-COCO 2017 데이터셋에서 다양한 Transformer 기반 Object Detector (DETR, Conditional-DETR, Anchor-DETR, DAB-DETR)에 IMFA를 적용하여 검증
- 기존 Multi-Scale 방식과 비교하여 계산 비용(FLOPs), FPS, GPU 메모리 사용량, Detection 성능(AP)을 비교 분석
- IMFA는 기존 대비 아주 소폭의 계산 증가로(약 +15GFLOPs, -3 FPS 수준) Detection 성능(AP, APS, APM, APL)을 일관되게 개선하였음을 입증
- 특히 작은 객체(AP_S)에 대해 기존 방법 대비 높은 성능 향상을 보여, Sparse Multi-Scale Sampling이 작은 객체 탐지에 효과적임을 입증
선택된 Location과 Level 시각화
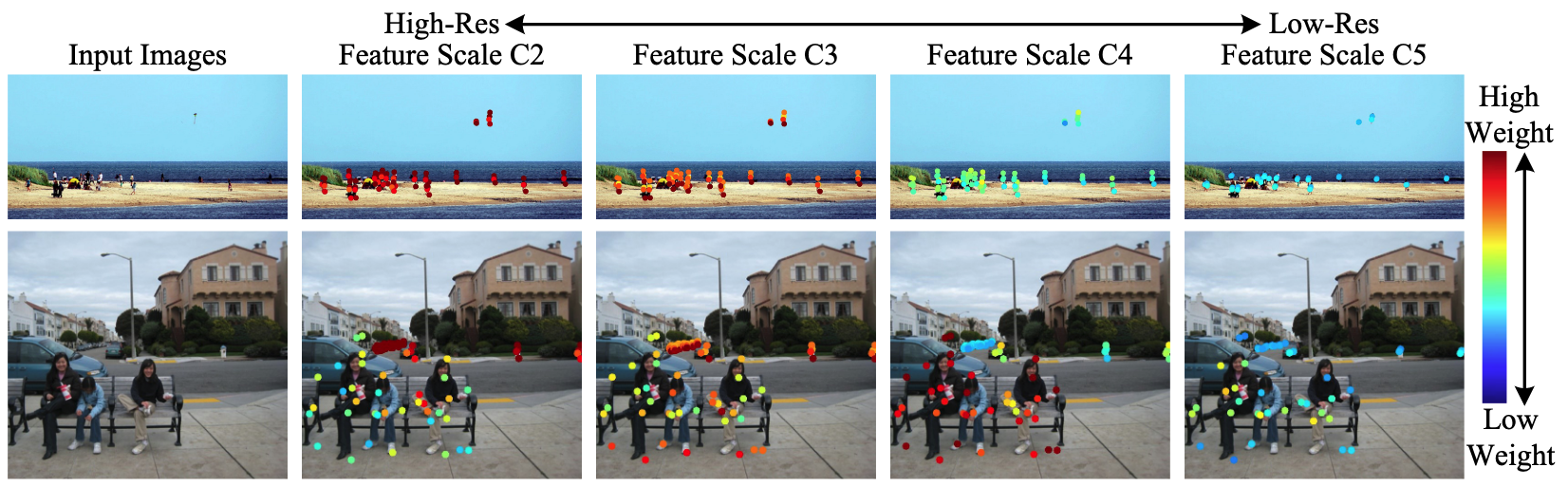

- Object 위주로 샘플링되는 것을 볼 수 있음 → 제안한 IMFA가 효과적임