TIES-Merging: Resolving Interference When Merging Models
Transfer learning – i.e., further fine-tuning a pre-trained model on a downstream task – can confer significant advantages, including improved downstream performance, faster convergence, and better sample efficiency. These advantages have led to a proliferation of task-specific fine-tuned models, which typically can only perform a single task and do not benefit from one another. Recently, model merging techniques have emerged as a solution to combine multiple task-specific models into a single multitask model without performing additional training. However, existing merging methods often ignore the interference between parameters of different models, resulting in large performance drops when merging multiple models. In this paper, we demonstrate that prior merging techniques inadvertently lose valuable information due to two major sources of interference: (a) interference due to redundant parameter values and (b) disagreement on the sign of a given parameter’s values across models. To address this, we propose our method, TRIM, ELECT SIGN & MERGE (TIES-MERGING), which introduces three novel steps when merging models: (1) resetting parameters that only changed a small amount during fine-tuning, (2) resolving sign conflicts, and (3) merging only the parameters that are in alignment with the final agreed-upon sign. We find that TIES-MERGING outperforms several existing methods in diverse settings covering a range of modalities, domains, number of tasks, model sizes, architectures, and fine-tuning settings. We further analyze the impact of different types of interference on model parameters, and highlight the importance of resolving sign interference
Problem:: 모델 병합 시 파라미터 간 간섭으로 인한 성능 저하 / 중복 파라미터와 부호 불일치로 유용한 정보 손실 / 태스크 수 증가 시 간섭 문제 심화
Solution:: 중복 파라미터 제거로 영향력 있는 파라미터 보존 / 부호 충돌 해결을 위한 투표 기반 부호 선택 / 선택된 부호와 일치하는 파라미터만 병합
Novelty:: 파라미터의 중요도를 고려하는 방식을 Task Vector 방식에 적용함
Note:: 제안 방식의 효용성을 여러 방면에서 잘 보여준 듯
Summary
Motivation
- 기존 Model Merging 방법은 단순 가중치 평균이나 가중합 사용 (Task Vector 기반)
- Task Vector
는 Fine-tuned 모델 가중치와 Pre-trained 모델 가중치의 차이로 정의: - 두 가지 주요 간섭 문제 발견:
- 중복 파라미터로 인한 간섭: 한 모델에서는 중요한 파라미터가 다른 모델에서는 중복(Redundant)으로 취급되어 가치 있는 정보 손실
- 부호 불일치로 인한 간섭: 동일한 파라미터가 서로 다른 모델에서 반대 부호를 가져 단순 평균화 시 성능 저하
- 이러한 간섭은 병합된 모델의 파라미터 크기를 감소시키고 미묘한 차이를 제거하여 전체 성능 저하 초래
Method
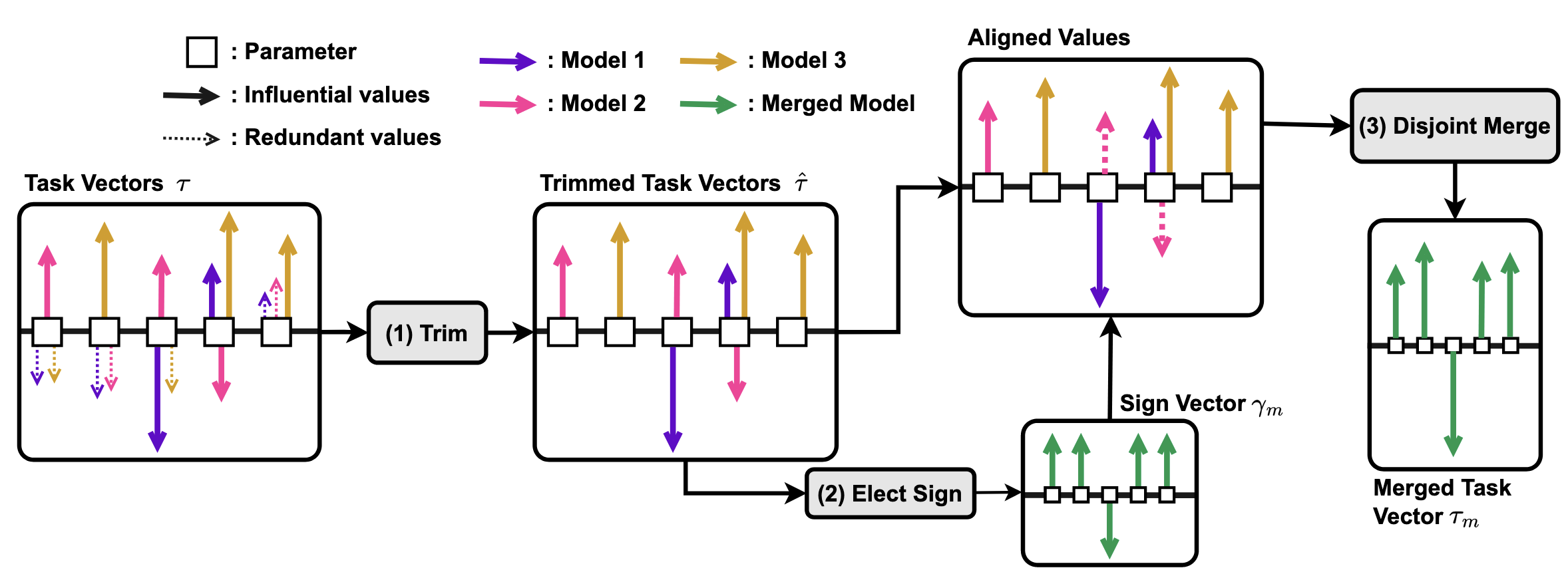
- TIES-MERGING: "TRIM, ELECT SIGN & MERGE"의 약자로, 세 단계 접근법으로 간섭 문제 해결
- TRIM: 각 태스크 벡터에서 중복(Redundant) 파라미터 제거
- 중요도에 따라 상위
%(예: 20%)의 파라미터만 유지하고 나머지는 0으로 설정 → 중요도는 Magnitude를 의미 - 이를 통해 중복 파라미터에 의한 간섭 제거
(부호 벡터와 크기 벡터로 분해)
- 중요도에 따라 상위
- ELECT SIGN: 파라미터별로 최종 부호 선택
- 각 파라미터
에 대해 양수와 음수 방향의 총 이동량 계산 - 더 큰 총 이동량을 가진 방향의 부호 선택
- 각 파라미터
- DISJOINT MERGE: 선택된 부호와 일치하는 파라미터 값만 평균화
- TRIM: 각 태스크 벡터에서 중복(Redundant) 파라미터 제거
- 최종 병합된 모델:
: 스케일링 하이퍼파라미터 : 최종 병합된 태스크 벡터
Method 검증
- 다양한 설정에서 실험 수행: NLP와 Vision 모달리티, 모델 크기, Fine-tuning 방식, 검증 세트 유무 등 다양한 조건에서 테스트
- NLP 태스크에서 최고 성능 대비 2.3% 절대적 향상 → TIES-MERGING이 기존 방법보다 간섭을 효과적으로 해결함을 입증
- Vision 태스크에서 최고 성능 대비 1.7% 절대적 향상 → 다양한 모달리티에서도 일관된 개선 효과 확인
- 검증 세트 없이도 ViT-B/32에서 6.6%, ViT-L/14에서 2.7% 향상 → 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 없이도 우수한 성능 달성
- Out-of-Domain 일반화 능력 실험: 태스크 7개로 학습된 모델을 6개의 보지 못한 태스크에서 평가
- T5-base에서 최고 기준선 대비 1.0% 향상 → 학습하지 않은 태스크에 대한 지식 전이 능력 확인
- T5-large에서 최고 기준선 대비 4.4% 향상 → 모델 크기가 커질수록 일반화 능력 더욱 향상
- 태스크 수 증가에 따른 확장성 실험: 2~7개 태스크를 병합하며 성능 변화 추적
- 태스크 수가 증가할수록 Task Arithmetic과의 성능 격차 확대 → TIES-MERGING이 다중 태스크 간섭을 더 효과적으로 해결
- 7개 태스크 병합 시 Simple Averaging 대비 15%p 이상 높은 성능 → 태스크 수 증가에 따른 확장성 입증
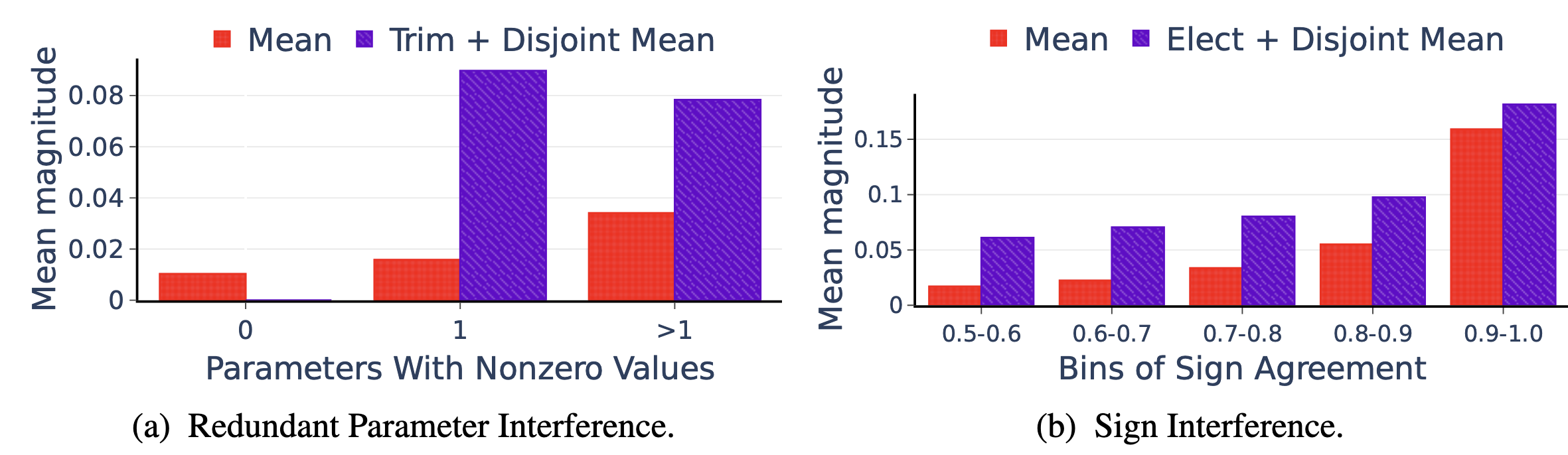
Mean Magnitude가 큼 → 파라미터가 영향력이 있음
(a): 0, 1, >1: 파라미터가 영향을 주는 태스크 수, 0은 Redundant를 의미
(b): 숫자는 부호의 일치 정도, 0.5는 +가 반 -가 반을 의미, 1은 모든 부호가 동일함
- 파라미터 간섭 영향 분석: 중복 파라미터와 부호 불일치가 병합된 파라미터 값에 미치는 영향 시각화
- 중복 파라미터 간섭 시 평균 크기 0.01에서 TRIM+DISJOINT MEAN 적용 후 0.08로 증가 → 중복 파라미터 제거가 중요 파라미터 값 보존에 효과적
- 부호 불일치 구간(0.5-0.6)에서 단순 평균 0.04, ELECT+DISJOINT MEAN 적용 후 0.15로 증가 → 부호 선택 과정이 불일치 문제 해결에 효과적
- 모든 간섭 유형에서 TIES-MERGING 적용 시 파라미터 다양성(표준편차) 증가 → 효과적인 파라미터 병합으로 정보 보존 능력 향상
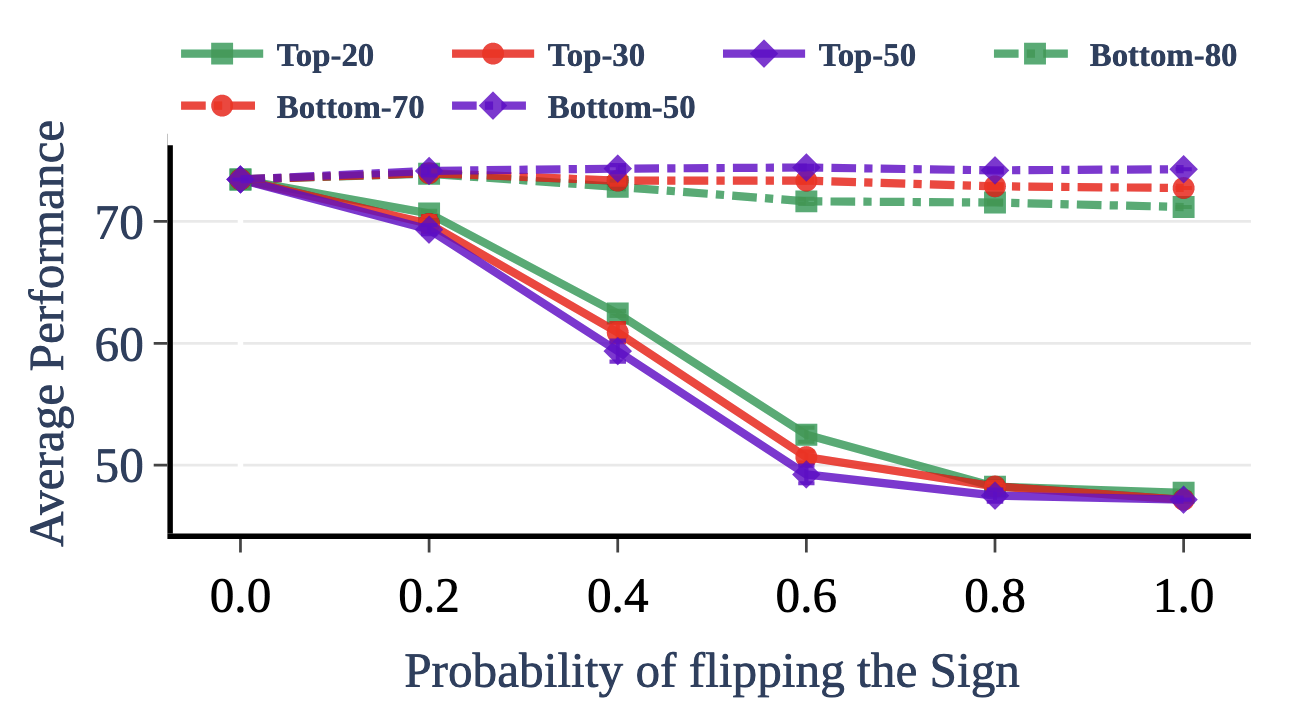
- 파라미터 부호 중요성 실험: 상위/하위 k% 파라미터의 부호를 확률적으로 반전시켜 성능 변화 측정
- 상위 20-30% 파라미터의 부호를 반전시키면 성능이 50%까지 하락 → 중요 파라미터의 올바른 부호 선택이 핵심
- 하위 70-80% 파라미터의 부호 변경은 성능에 거의 영향 없음 → 중복 파라미터 제거의 타당성 입증
- Oracle 부호 벡터 테스트: 다중태스크 학습 모델에서 부호 벡터를 추출하여 TIES-MERGING에 적용 → 이상적인 부호 벡터를 이용한 경우
- 다중태스크 모델의 부호 벡터 사용 시 72.0% 성능 달성(다중태스크 모델 73.1%) → 올바른 부호 선택으로 다중태스크 모델에 근접 가능
- 기존 TIES-MERGING 66.4% 대비 5.6% 향상 → 부호 추정 방법 개선으로 추가 성능 향상 가능성 시사
- 방법 구성요소 분석: TIES-MERGING의 각 구성요소를 하나씩 제거하며 성능 변화 측정
- TRIM 제거 시 T5-base에서 1.5%p, (IA)³에서 0.1%p 하락 → 중복 파라미터 제거의 효과 확인
- ELECT SIGN 제거 시 T5-base에서 0.8%p, (IA)³에서 1.1%p 하락 → 부호 선택의 중요성 입증
- DISJOINT MERGE 제거 시 T5-base에서 1.9%p, (IA)³에서 3.2%p 하락 → 선택된 부호와 일치하는 파라미터만 병합하는 과정의 핵심적 역할 확인
- 스케일링 제거 시 T5-base에서 2.5%p, (IA)³에서 5.2%p 하락 → 적절한 스케일링이 병합 성능에 결정적 영향