Scaling and evaluating sparse autoencoders
Sparse autoencoders provide a promising unsupervised approach for extracting interpretable features from a language model by reconstructing activations from a sparse bottleneck layer. Since language models learn many concepts, autoencoders need to be very large to recover all relevant features. However, studying the properties of autoencoder scaling is difficult due to the need to balance reconstruction and sparsity objectives and the presence of dead latents. We propose using k-sparse autoencoders [Makhzani and Frey, 2013] to directly control sparsity, simplifying tuning and improving the reconstruction-sparsity frontier. Additionally, we find modifications that result in few dead latents, even at the largest scales we tried. Using these techniques, we find clean scaling laws with respect to autoencoder size and sparsity. We also introduce several new metrics for evaluating feature quality based on the recovery of hypothesized features, the explainability of activation patterns, and the sparsity of downstream effects. These metrics all generally improve with autoencoder size. To demonstrate the scalability of our approach, we train a 16 million latent autoencoder on GPT-4 activations for 40 billion tokens. We release training code and autoencoders for open-source models, as well as a visualizer.
Problem:: 기존 희소 오토인코더(SAE)의 스케일링 어려움 / 재구성(Reconstruction)과 희소성(Sparsity) 간의 균형 문제 및 Dead Latent 문제 발생
Solution:: L1 페널티 대신 TopK 활성화 함수를 사용하여 희소성을 직접 제어 / Encoder-Decoder 가중치 초기화 및 Auxiliary Loss를 도입하여 Dead Latent 방지
Novelty:: TopK 활성화 함수와 Dead Latent 방지 기법을 결합하여 대규모 SAE를 안정적으로 훈련하는 방법론 제시 / 재구성 손실 외 Downstream Loss, Probe Loss 등 새로운 질적 평가 지표 제안 및 검증
Note:: 오토인코더의 크기가 클수록 학습된 Feature의 질이 전반적으로 향상됨 / 학습된 Feature는 기존 모델의 채널보다 훨씬 희소하고(sparse) 해석 가능한 효과를 가짐 (Ablation 효과 10-14% vs 60%) / TopK 방식은 L1 페널티의 부작용인 Activation Shrinkage를 방지함
Summary
Motivation
- 언어 모델 해석가능성의 필요성
- 블랙박스 문제: GPT-4 같은 대규모 언어 모델의 내부 동작 메커니즘 이해 어려움
- 실용적 중요성: AI 안전성, 편향 탐지, 모델 동작 예측을 위한 내부 메커니즘 해석 필수
- Sparse Autoencoder 개념
- 기본 목적: 언어 모델의 내부 활성화에서 해석 가능한 특성들을 추출
- 작동 방식:
- 언어 모델 특정 층의 고차원 벡터를 입력으로 받음
- 더 많은 수의 sparse한 특성으로 분해하여 각각이 명확한 의미를 가지도록 함
- 예시: "프랑스 관련", "부정적 감정", "수학적 개념" 등의 개별 특성으로 분리
- 기존 방법의 한계
- 규모 문제:
- 언어 모델이 학습하는 개념 수가 매우 방대 (수백만 개 이상)
- 기존 연구는 작은 모델에서 작은 autoencoder로만 실험
- 기술적 문제:
- Dead Latent 문제: 훈련 중 일부 뉴런이 아예 활성화되지 않아 최대 90%의 용량 낭비
- L1 Penalty 한계: 모든 활성화 값을 0으로 축소시키는 편향 존재
- 평가 메트릭 부족: Reconstruction 성능만으로는 실제 해석가능성 평가 불가
- 규모 문제:
Method
-
Sparsity 제어를 위해 L1 패널티 대신 TopK 활성화 함수를 사용하는 k-sparse autoencoder를 제안
-
이 방식은 활성화되는 Latent의 수를
로 직접 제어하여 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝을 단순화하고 Reconstruction-Sparsity Trade-off를 개선함 -
Encoder의 수식은 다음과 같음:
-
-
Dead Latent 문제를 해결하기 위해 두 가지 주요 기법을 도입
- Encoder 가중치를 Decoder 가중치의 Transpose로 초기화
- Dead Latent를 사용하여 Reconstruction Error를 모델링하는 Auxiliary Loss (AuxK)를 추가
-
이 기법들을 통해 1600만개의 Latent를 가진 대규모 Autoencoder에서도 Dead Latent 비율을 7% 미만으로 유지
Method 검증
실험 1: Scaling Laws
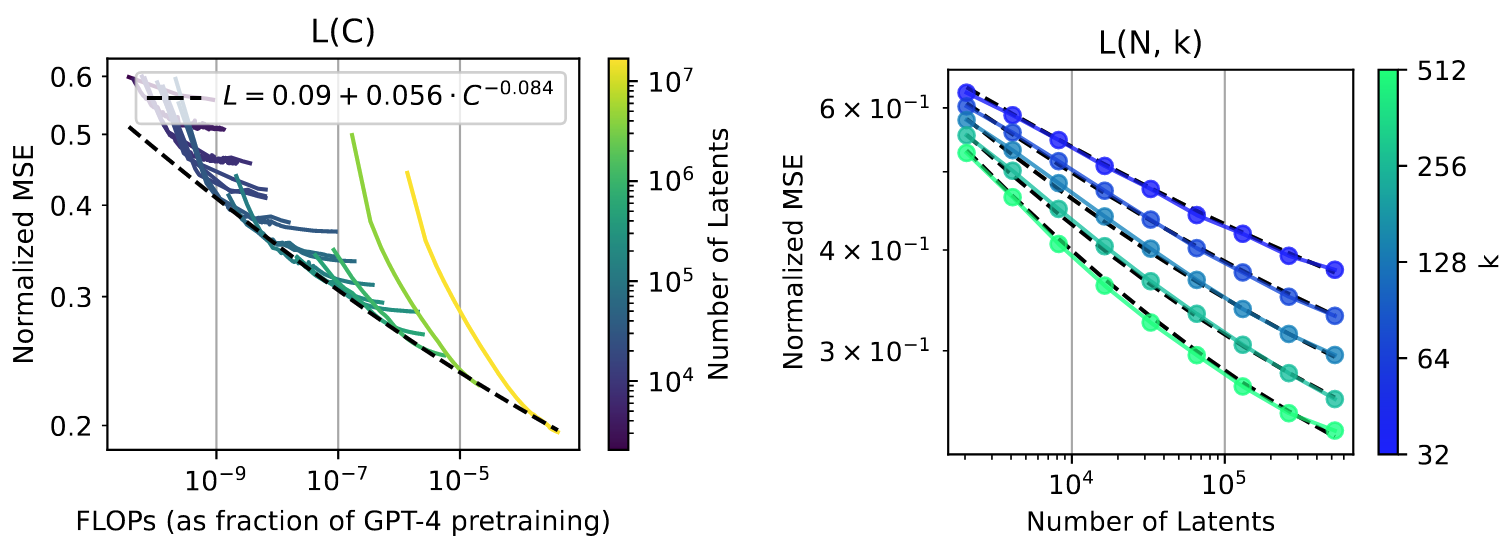
L(C)와 L(N, K)
- Training to compute-MSE frontier (L(C)): 주어진 계산량 예산 내에서 최적의 MSE를 달성하도록 학습
- 결과: MSE는 사용된 계산량에 대해
와 같은 거듭제곱 법칙(power law)을 따름 - 통찰: 이 접근법은 SAE의 목표(좋은 feature 학습)와 완전히 부합하지는 않음. Latent 수가 많으면 낮은 MSE 달성이 더 쉽기 때문에 다른 크기의 모델 간 공정한 비교가 어려움
- 결과: MSE는 사용된 계산량에 대해
- Jointly fitting sparsity (L(N,K)): Latent의 수(
n)와 희소성 수준(k)을 동시에 고려하는 통합된 스케일링 법칙을 도출-
결과 (통합 스케일링 법칙): GPT-4 오토인코더에 대한 법칙은 다음과 같음
-
통찰: 수식의 계수들을 통해
k값이 클수록(덜 희소할수록)n을 늘렸을 때 MSE가 더 빠르게 개선되고(), 줄일 수 없는 손실이 감소( )하는 경향을 확인함
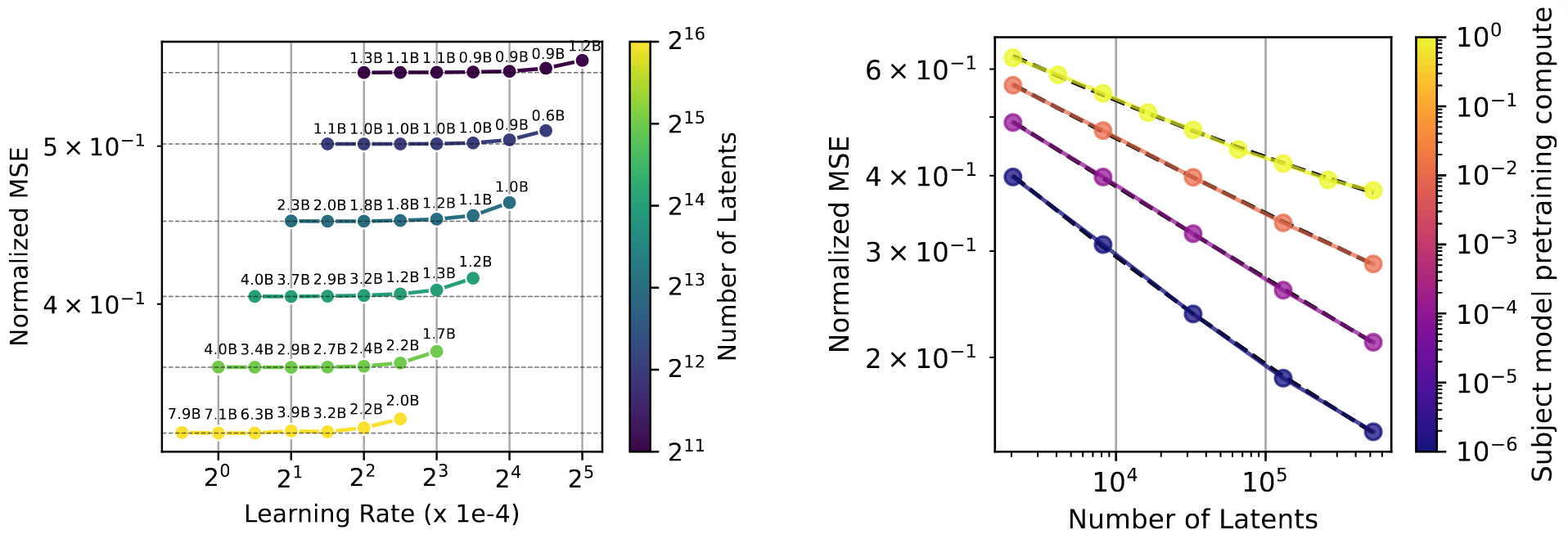
-
L(N)과 Subject Model Size
- Training to convergence (L(N)): 계산 효율성을 무시하고, 모델이 완전히 수렴할 때까지 학습하여 달성 가능한 최상의 재구성 성능을 확인
- 결과: 수렴에 필요한 토큰 수는 Latent 수(
n)에 따라 GPT-4 기준 약로 증가하며, 수렴 가능한 최대 학습률은 에 비례하여 감소함 - 통찰: 오토인코더 크기가 커질수록 수렴에 더 많은 데이터가 필요하지만, 예측 가능한 관계로 확장됨
- 결과: 수렴에 필요한 토큰 수는 Latent 수(
- Subject Model Size: 대상 언어 모델의 크기를 키워가며 SAE의 성능 변화를 측정
- 결과: 더 큰 언어 모델은 동일한 MSE를 달성하기 위해 더 큰 오토인코더(더 많은 Latent)를 필요로 하며, 스케일링 효율도 더 나빠짐
- 통찰: 언어 모델이 커질수록 그 내부를 표현하는 데 필요한 SAE의 복잡도도 함께 증가함
- Irreducible Loss (줄일 수 없는 손실): 스케일링 법칙의 정확도를 높이기 위해, 모델을 아무리 키워도 더는 줄어들지 않는 오차의 하한선인 '줄일 수 없는 손실' 항을 수식에 추가함
의 - 결과: 이 항을 추가했을 때 스케일링 법칙의 적합도(quality of fit)가 크게 향상됨
- 통찰: 이는 모델 활성화(activation) 내에 구조화된 부분과 함께 노이즈처럼 모델링이 매우 어려운 비구조적인 부분이 섞여있기 때문일 것으로 추정됨. 이 비구조적인 부분이 손실의 하한선을 형성함
실험 2: Downstream Loss
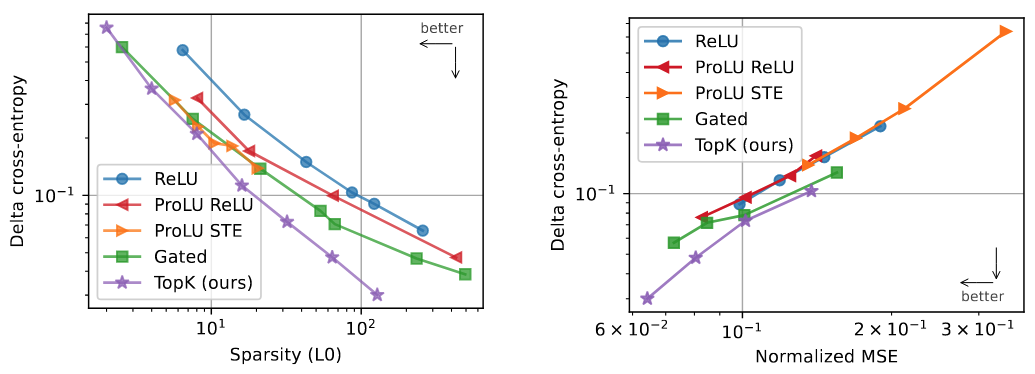
왼쪽은 Latent 수를 고정했을 때, 오른쪽은 Sparsity Level을 고정 했을 때의 성능
- 실험 진행 방법: 언어 모델의 Forward Pass 중 원본 Residual Stream Activation을 SAE가 재구성한 값으로 대체하고, 모델의 최종 Cross-Entropy Loss 변화를 측정
- 비교군: ReLU, ProLU, Gated 등 다른 활성화 함수를 사용한 SAE
- 정량적 성능: 동일한 MSE 수준에서, TopK Autoencoder가 다른 방법들보다 더 낮은 Downstream Loss를 달성함
- 통찰: TopK SAE가 재구성한 Feature가 언어 모델의 행동에 더 중요한 정보를 담고 있음을 의미함 → SAE가 재구성한 정보로 바꿔치기해도, 언어 모델이 원래 하려던 작업을 거의 비슷하게 수행할 수 있음
실험 3: Probe Loss (Feature Recovery)
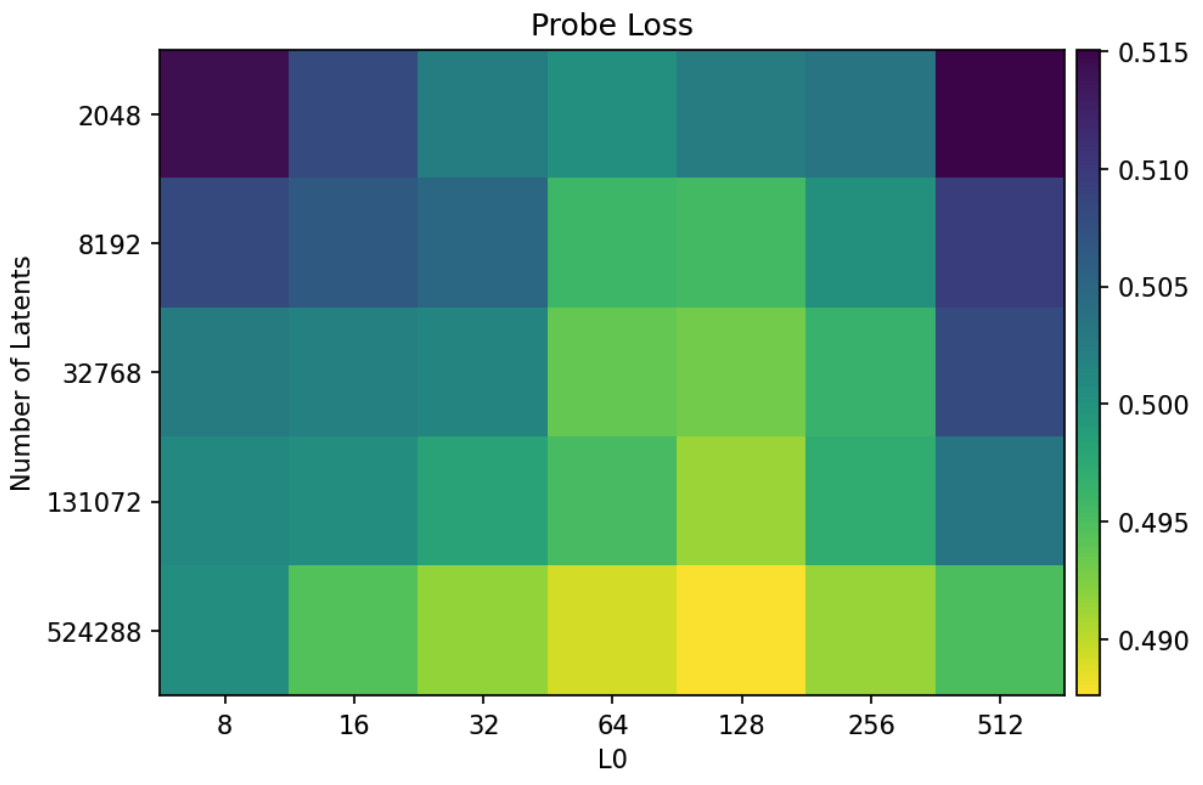
- 실험 진행 방법: SAE가 학습한 각 Latent에 대해 1D Logistic Probe를 훈련하여, 미리 정의된 61개의 이진 분류 작업(예: 감성 분석)을 얼마나 잘 수행하는지 평가
- 비교군: ReLU 기반 SAE, Residual Stream 채널 직접 사용
- 정량적 성능: 전체 Latent 수가 증가할수록 Probe Loss가 개선(감소)됨. TopK는 ReLU나 Residual Stream 채널을 직접 사용하는 것보다 월등한 성능을 보임 → SAE가 학습한 Feature 하나하나가 '감성', '주제' 등 인간이 생각하는 특정 개념과 명확하게 일치하는 경향이 더 강해짐
- 통찰: 더 큰 TopK Autoencoder는 사람이 가설로 세운 유의미한 Feature들을 더 잘 복원함
실험 4: Explainability (N2G)
- 실험 진행 방법: N-gram 기반 설명 모델인 Neuron to Graph (N2G)를 사용하여 각 Latent의 활성화 패턴을 설명하고, 그 설명의 Precision과 Recall을 측정
- 비교군: ReLU 기반 SAE
- 정량적 성능: TopK 모델은 ReLU 모델에 비해 Recall이 1.5배 이상 높고 Precision은 약간만 낮아(0.9배 이상) 전반적인 F1 점수가 더 높음 → SAE가 학습한 Feature가 언제 활성화되는지 "이런 단어가 나오면 켜진다"와 같은 단순한 규칙으로 더 정확하게 설명할 수 있게 됨
- 통찰: TopK로 학습된 Feature는 더 단일 의미적(Monosemantic)이며, 작은 활성화 값을 0으로 만들어 노이즈가 적기 때문에 더 간단하고 명확한 설명이 가능함
실험 5: Sparsity of Ablation Effects
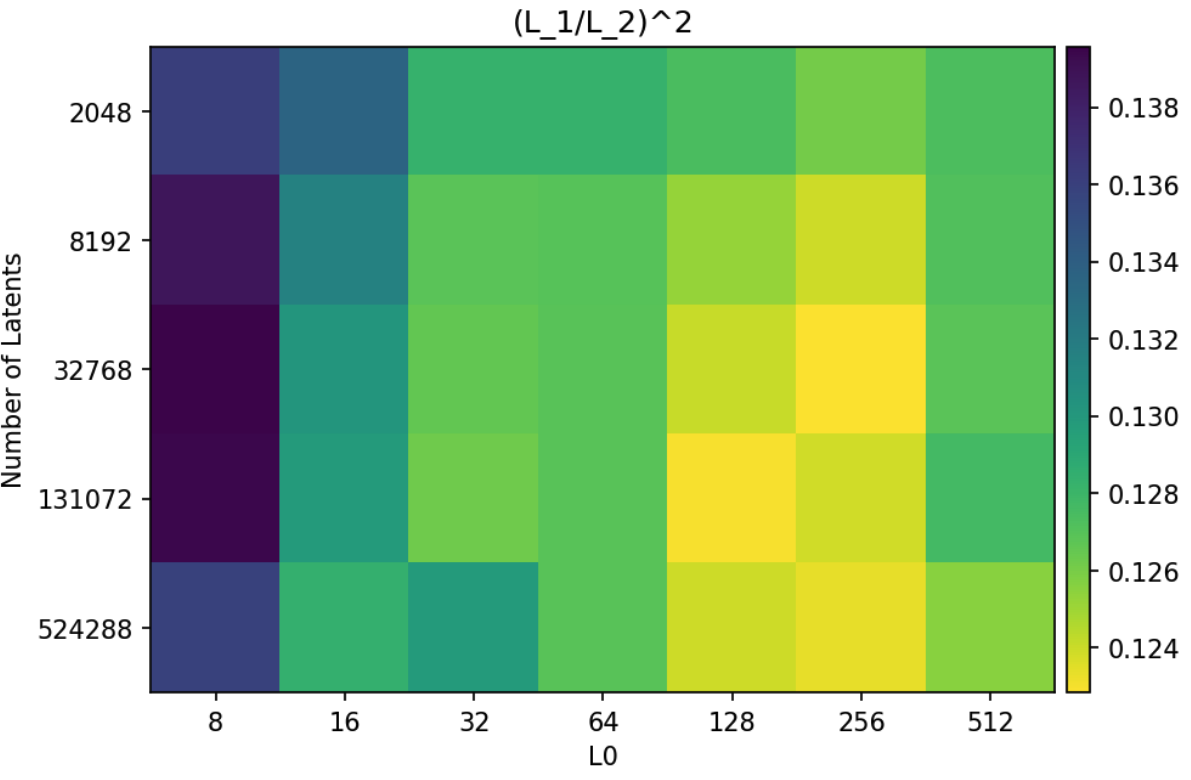
- 실험 진행 방법: 각 Latent를 개별적으로 Ablation(제거)했을 때, 모델의 최종 Logits에 미치는 영향이 얼마나 Sparse한지를
지표로 측정 - 비교군: Residual Stream 채널 Ablation
- 정량적 성능: Autoencoder Latent의 Ablation 효과는 Residual Stream 채널을 직접 Ablation하는 것보다 훨씬 Sparse함 (10-14% vs 60%). 활성 Latent 수(
k)가 증가할수록 효과가 더 Sparse해지는 경향을 보임 → SAE의 일부 제거는 Logit의 10~14%만 영향을 미치지만 원본 Feature는 60%에 영향을 미침 - 통찰: 학습된 Feature들이 모델의 출력에 지역적이고 Sparse한 영향을 미치는, 해석 가능한 단위에 해당함을 시사함
추가 분석: TopK Activation Function
Activation Shrinkage
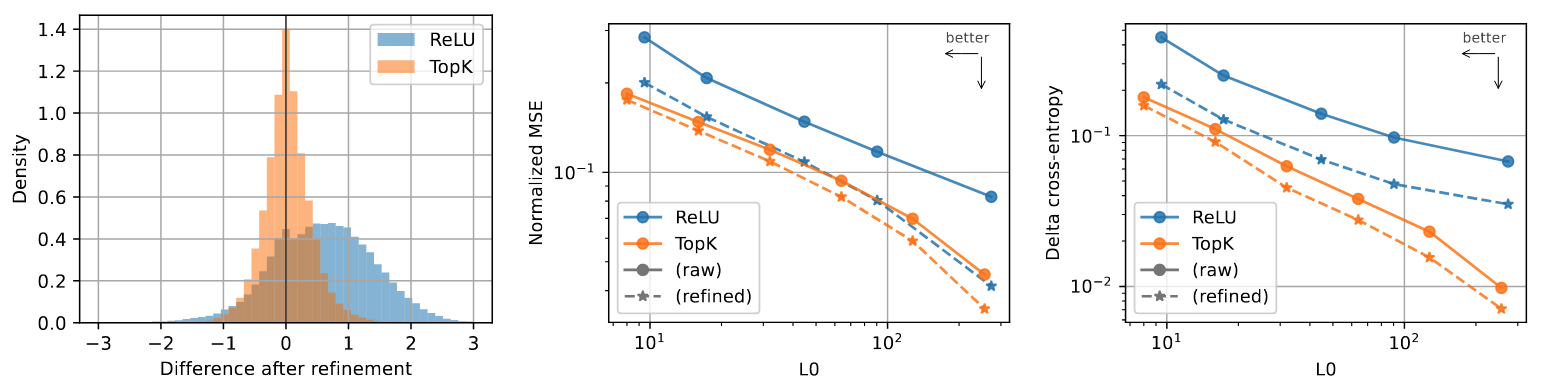
- 실험 진행 방법:
페널티가 활성화(activation) 값의 크기를 줄이는 부작용(Activation Shrinkage)이 있는지 확인하기 위해, 학습된 디코더(Decoder)는 고정한 채 최적의 활성화 값을 다시 계산(refinement)하여 기존 값과 비교함 → Refinement: 학습에 사용된 Latent들을 그대로 이용하되, 복원 성능이 최소화되도록 Latent의 크기를 최적화 - 정량적 성능: ReLU 모델의 활성화 값은 재계산 후 평균적으로 커지는 경향을 보인 반면, TopK 모델의 활성화 값은 거의 변하지 않았음 →
방식은 모든 신호를 약하게 만드는 부작용이 있지만, TopK는 중요한 신호만 골라내고 그 세기는 그대로 유지함. - 통찰: TopK가 활성화 값의 크기를 왜곡하지 않고 희소성을 직접 제어하는 더 나은 방법임을 확인함. 이 보정 과정이 성능을 일부 개선하지만, 여전히 TopK와 ReLU 모델 간의 근본적인 성능 차이를 모두 메우지는 못함.
다른 활성화 함수와의 비교
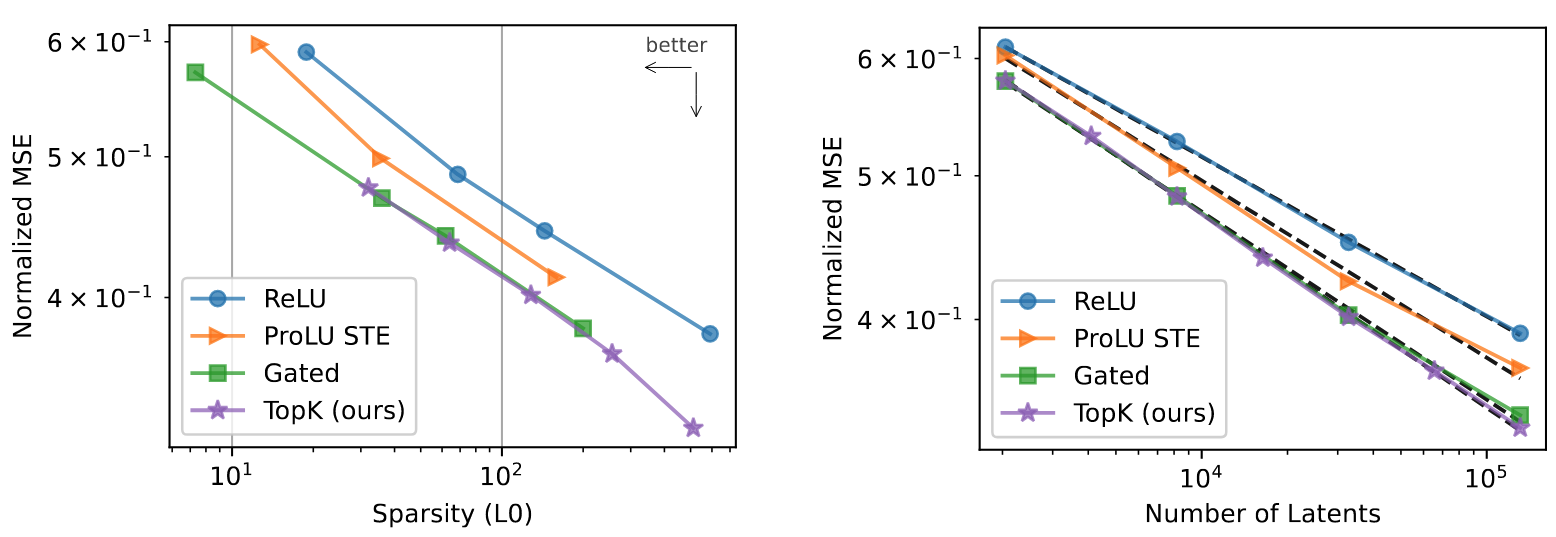
왼쪽은 Latent 수를 고정했을 때, 오른쪽은 Sparsity Level을 고정 했을 때의 성능
- 실험 진행 방법: Activation Shrinkage 문제를 해결하기 위해 제안된 다른 최신 방법들(Gated SAEs, ProLU)과 재구성-희소성 성능을 비교함.
- 정량적 성능: 비교된 모든 방법들이 기존 ReLU +
방식보다 성능이 좋았지만, 전반적으로 TopK가 재구성-희소성 측면에서 가장 좋은 성능을 보임 → 여러 최신 기술과 비교해도, TopK 방식이 성능과 희소성 두 마리 토끼를 가장 잘 잡음. - 통찰: TopK는 희소 오토인코더를 위한 매우 효과적이고 경쟁력 있는 활성화 함수임.
Progressive Recovery
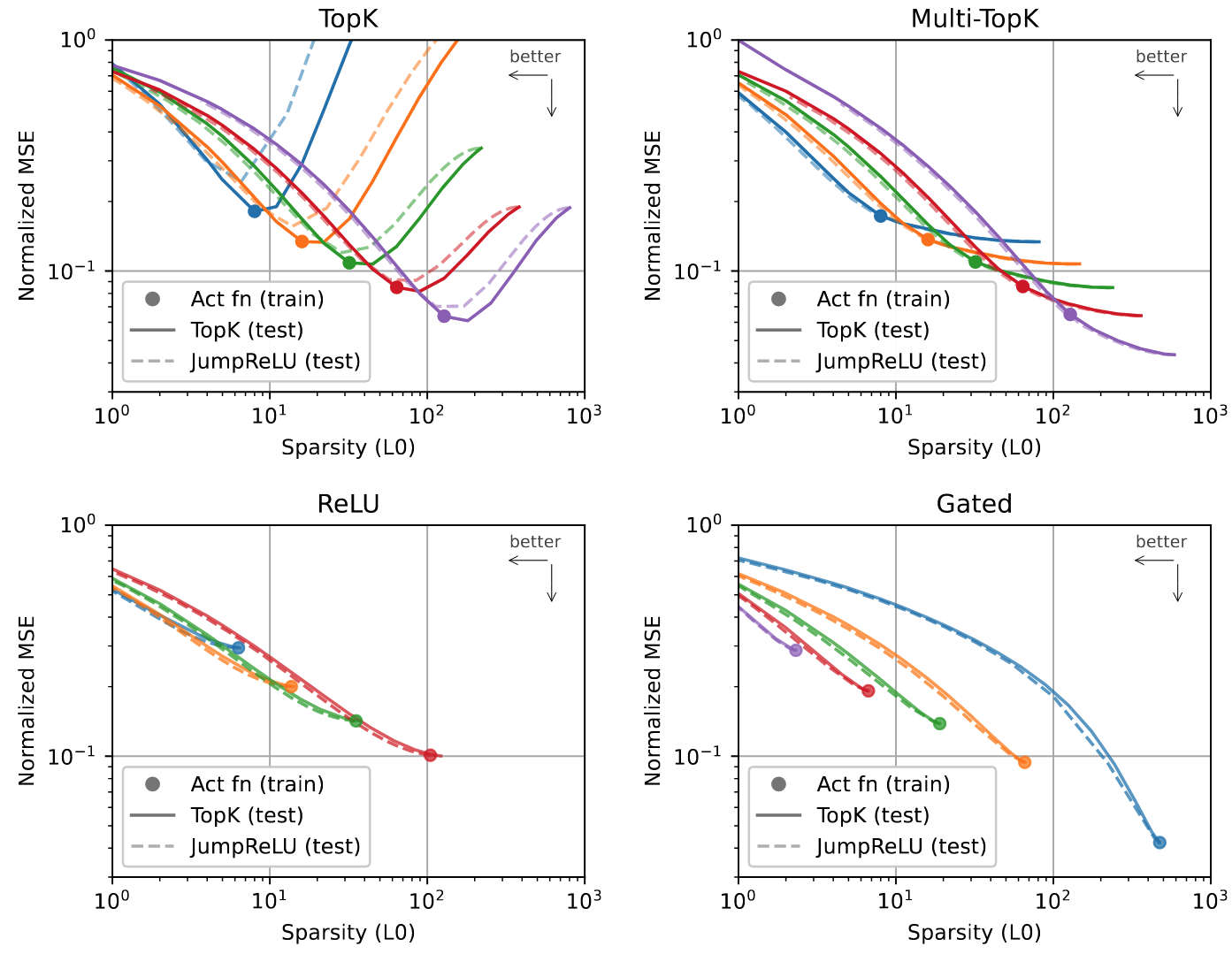
- 실험 진행 방법: 좋은 오토인코더는 가장 중요한 소수의 Feature만으로도 정보를 잘 복원하는 'Progressive Code'를 학습해야 함. 이를 확인하기 위해 학습 시 사용한 활성 Latent 수(
k)와 다른k'값으로 테스트 시간에 성능을 평가함 - 정량적 성능: 일반적인 TopK 모델은 학습에 사용된 특정
k값에 과적합(overfitting)되어, 테스트 시k보다 훨씬 큰 값을 사용하면 성능이 저하됨. 반면, 여러k값에 대한 손실을 함께 사용하는 Multi-TopK 방식은 다양한k'값에 대해 더 나은 일반화 성능을 보임 → 일반 TopK는 'k개만 고르기'에만 익숙해져 다른 개수에는 취약하지만, Multi-TopK는 여러 상황을 함께 학습시켜 유연성을 높임. - 통찰: Multi-TopK로 학습하면, 테스트 시에 고정된 수의 Latent(
TopK)를 사용하든, 고정된 임계값(JumpReLU)을 사용해 동적으로 Latent 수를 결정하든 성능 저하 없이 모델을 유연하게 사용할 수 있음.