Towards Task-Conflicts Momentum-Calibrated Approach for Multi-task Learning
Multi-task learning (MTL) has succeeded in various industrial applications by utilizing common knowledge among joint training tasks to enhance the generalization of MTL models, resulting in improved performance across all training tasks simultaneously. Unfortunately, training all tasks simultaneously often causes performance degradation compared to single-task models since different tasks might conflict with each other. Despite existing MTL methods that aim to mitigate task conflicts by manipulating task gradients at each iteration, they ignore the potential influence of noisy data from different batches on task gradients. Consequently, the current iteration's task gradient may not accurately reflect the task itself, leading to inadequate alleviation of the dilemma of task conflicts. Moreover, existing works seldom explore the potential source of task conflicts and merely pose an assumption. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth empirical investigation into the potential sources of performance degradation of MTL and find that task gradient conflict is one of the primary reasons for the performance degradation of tasks. Then, to address the task conflicts problem, we propose a novel gradient manipulation approach, namely MoCoGrad, which manipulates task gradients by leveraging the momentum information of the task to calibrate the gradients of conflicting tasks. In addition, we derive theoretical guarantees for the convergence of our proposed MoCoGrad and theoretically analyze the convergence rate of MoCoGrad. Finally, to evaluate the effectiveness of MoCoGrad, extensive experiments are conducted on six real-world datasets from different domains. Our approach yields the best performance across all tasks in all six MTL benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
Problem:: 기존 연구들은 Gradient Conflict를 MTL 성능 저하의 원인으로 지목하면서도 분석하지 않음/기존 방법들이 현재 Iteration의 Gradient만 고려하여 Noisy Data 영향에 취약함
Solution:: Task Conflict와 Gradient Conflict의 관게 규명/Task의 Momentum 정보를 활용하여 Conflicting Gradient를 보정(calibrate)하는 MoCoGrad 제안
Novelty:: 작업 간 충돌 원인에 대한 체계적 분석 및 정량화
Note:: TCI와 GCD를 GazeTargetDetection의 두 Task간의 충돌 정도를 나타내는데 이용해 볼 수 있을듯
Summary
Motivation
- Multi-Task Learning(MTL)은 여러 작업을 동시에 학습하여 공통 지식을 활용함으로써 개별 작업의 성능을 향상시키는 접근법
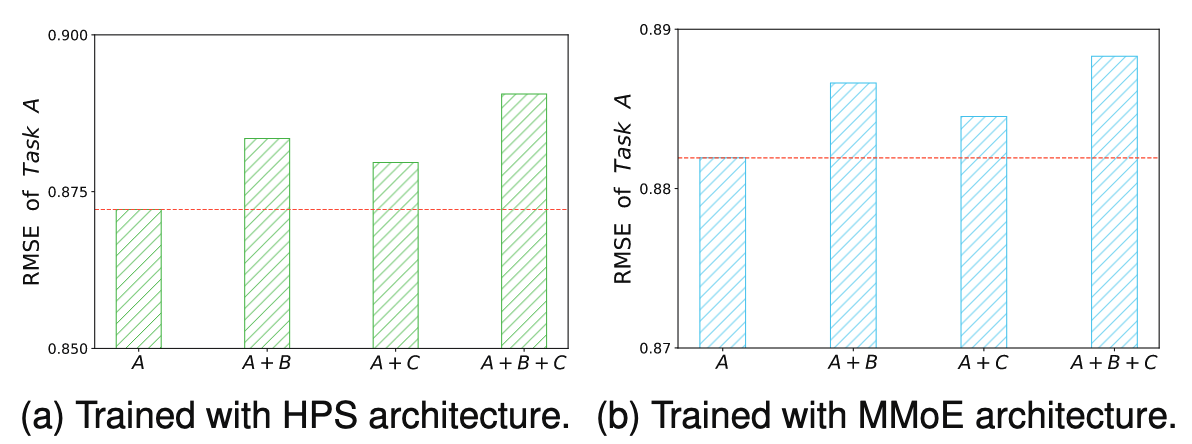
HPS와 MMoE는 MTL을 위한 아키텍쳐
- 서로 다른 작업을 동시에 학습하면 작업 간 충돌(Task Conflict)이 발생하여 단일 작업 학습보다 성능이 저하되는 문제 발생
- 이를 확인하기 위해 MovieLens 데이터셋에서 실험한 결과, 동시에 학습하는 작업 수가 증가할수록 특정 작업(Task A)의 성능이 더 악화됨
- 기존 연구들은 Task Conflict 문제를 다루기 위해 두 가지 접근법 제시:
- 소프트 파라미터 공유 방식(태스크 별로 독립적이지만 정보 교환 발생)의 MTL 네트워크 구조 설계 (MMoE, MTAN 등)
- 하드 파라미터 공유 방식(공통 네트워크와 분리된 네트워크가 존재)에서 최적화 관점으로 접근 (PCGrad, GradVac 등)
- 그러나 기존 연구들의 한계:
- Task Conflict의 원인에 대한 정량적, 심층적 분석 부족
- 현재 배치 데이터에서 도출된 Gradient만 고려하여 노이즈에 취약
Method
Task Conflicts Analysis
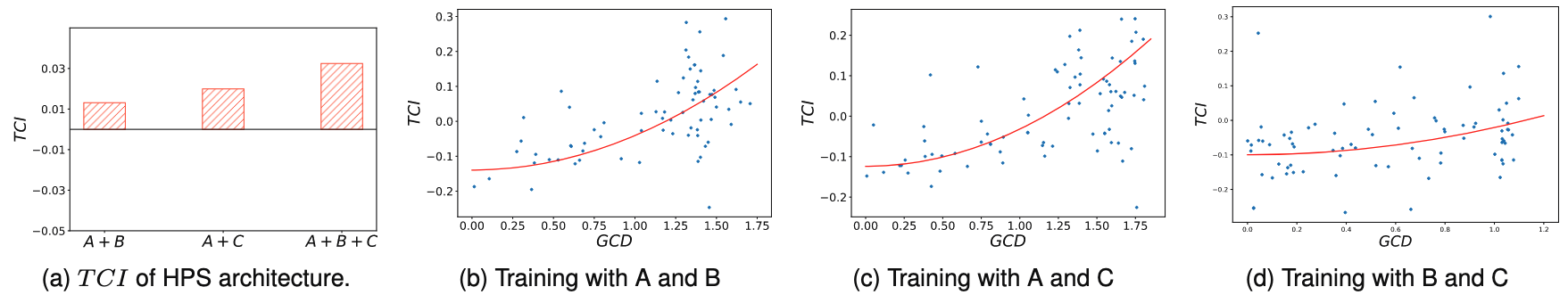
Task Conflict와 Gradient Conflict가 강한 상관관계를 보임 → 우리가 처음으로 이거 보였음! 다른 애들은 그냥 대강 보이더라
- Task Conflict를 정량적으로 측정하기 위한 TCI(Task Conflict Intensity) 정의:
: 작업 에 대한 기대 위험 - 음수 TCI는 Task Conflict가 발생했음을 의미
- Gradient Conflict를 측정하기 위한 GCD(Gradient Conflict Degree) 정의:
: 두 task gradient 간의 각도 - GCD > 1일 때 gradient conflict 발생
Momentum-calibrated Conflicting Gradients (MoCoGrad)
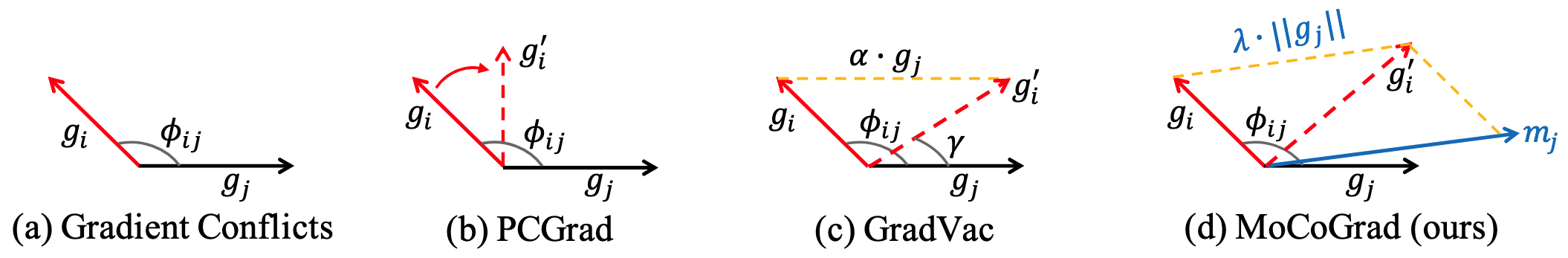
기존 방식은 한 배치 기준으로 계산 → 배치 별로 보정되는 방향이 다른데, 너무 노이즈가 심함
- 제안하는 MoCoGrad 방법은 작업의 momentum 정보를 활용하여 충돌하는 gradient를 보정
- MoCoGrad 알고리즘의 핵심:
- 두 작업의 gradient
, 간 conflict가 발생(GCD > 1)하면 momentum 정보를 활용하여 보정 - 보정된 gradient:
: 보정 정도를 제어하는 하이퍼파라미터 : j-task의 t 시점 momentum ( )
- 두 작업의 gradient
- MoCoGrad 알고리즘:
- 각 작업의 gradient 계산
- 무작위 순서로 작업 쌍을 선택하여 GCD 계산
- GCD > 1인 경우 momentum 정보를 활용하여 충돌 gradient 보정
- 모든 작업에 대해 반복한 후 보정된 Gradient로 파라미터 업데이트
Method 검증
- 이론적 분석:
- MoCoGrad의 수렴성 증명 (Theorem 2)
수렴 속도 분석 (Corollary 1)
- 6개 데이터셋에서 실험적 검증:
- 추천 시스템: AliExpress(CTR, CTCVR 예측), MovieLens(영화 평점 회귀)
- 양자 화학: QM9(분자 그래프 회귀)
- 컴퓨터 비전: NYUv2, CityScape(장면 이해), Office-Home(이미지 분류)
- 주요 실험 결과:
- AliExpress: 8개 작업 중 8개에서 최고 성능, 평균 0.48% 성능 향상
- MovieLens: RMSE 기준 2.93% 성능 향상
- QM9: MAE 기준 32.30% 성능 향상
- NYUv2: 10개 메트릭 중 7개에서 최고 성능, 9.65% 성능 향상
- CityScape: 모든 작업에서 최고 성능, 9.93% 성능 향상
- Office-Home: 모든 도메인에서 최고 성능
- Ablation Study:
- Momentum 정보 활용의 중요성 검증
- 여러 MTL 아키텍처와 결합 시에도 성능 향상 확인
- 역전파 시간 비교에서 경쟁력 있는 효율성 입증