Localizing and Editing Knowledge In Text-to-Image Generative Models
Text-to-Image Diffusion Models such as Stable-Diffusion and Imagen have achieved unprecedented quality of photorealism with state-of-the-art FID scores on MS-COCO and other generation benchmarks. Given a caption, image generation requires fine-grained knowledge about attributes such as object structure, style, and viewpoint amongst others. Where does this information reside in text-to-image generative models? In our paper, we tackle this question and understand how knowledge corresponding to distinct visual attributes is stored in large-scale text-to-image diffusion models. We adapt Causal Mediation Analysis for text-to-image models and trace knowledge about distinct visual attributes to various (causal) components in the (i) UNet and (ii) text-encoder of the diffusion model. In particular, we show that unlike large-language models, knowledge about different attributes is not localized in isolated components, but is instead distributed amongst a set of components in the conditional UNet. These sets of components are often distinct for different visual attributes (e.g., style} / objects). Remarkably, we find that the text-encoder in public text-to-image models such as Stable-Diffusion contains {\it only} one causal state across different visual attributes, and this is the first self-attention layer corresponding to the last subject token of the attribute in the caption. This is in stark contrast to the causal states in other language models which are often the mid-MLP layers. Based on this observation of only one causal state in the text-encoder, we introduce a fast, data-free model editing method DiffQuickFix which can effectively edit concepts (remove or update knowledge) in text-to-image models. DiffQuickFix can edit (ablate) concepts in under a second with a closed-form update, providing a significant 1000x speedup and comparable editing performance to existing fine-tuning based editing methods.
Problem:: 텍스트-이미지 생성 모델에서 다양한 시각적 속성(객체, 스타일, 색상, 행동 등)에 관한 지식이 어디에 저장되어 있는지 이해 부족 / 모델에서 특정 개념을 편집하기 위한 효율적인 방법 필요
Solution:: Causal Mediation Analysis를 통해 UNet과 텍스트 인코더에서 다양한 시각적 속성 지식의 위치 파악 / 텍스트 인코더의 첫 번째 Self-Attention 레이어에 지식이 집중되어 있다는 발견을 활용한 DIFF-QUICKFIX 모델 편집 방법 제안
Novelty:: 텍스트-이미지 모델의 지식이 UNet에서는 분산되어 있고 텍스트 인코더에서는 단일 레이어에 집중되어 있다는 새로운 발견
Note:: 후속 연구중 하나는 Nudity와 같은 개념은 Text Encoder의 여러 층을 학습시켜야 동작함을 보이며 해당 개념이 더 어렵다고 주장 → 논문의 실험은 명확한 주제들을 편집하려고 했기 때문에 첫 번째 레이어만 활성화 된 걸로 볼 수 있을 듯 / Unet의 경우 특정 지식이 여러곳에 분산되어 저장 → 공격의 여지가 많고 방어하기 힘듦을 의미? → 실제로 Text Encoder를 학습시키면 Unet 학습 보다 ASR이 좋아짐
Summary
Motivation
- 텍스트-이미지 생성 모델은 객체 구조, 스타일, 시점 등 다양한 시각적 속성에 대한 세부적인 지식 필요
- LAION-5B와 같은 대규모 이미지-텍스트 쌍 데이터셋에서 훈련된 모델들은 다양한 시각적 개념을 기억
- 이전 연구들은 텍스트-이미지 모델이 훈련 데이터셋의 다양한 측면을 기억한다는 것을 입증
- 그러나 이러한 지식이 모델 내 어디에 어떻게 저장되어 있는지에 대한 이해 부족
- 서로 다른 시각적 속성(객체, 스타일, 색상, 행동 등)에 관한 지식의 위치를 이해하는 것이 중요
- 특히 GPT와 같은 언어 모델과 텍스트-이미지 모델의 지식 저장 패턴 차이에 대한 분석 필요
Method
Causal Mediation Analysis
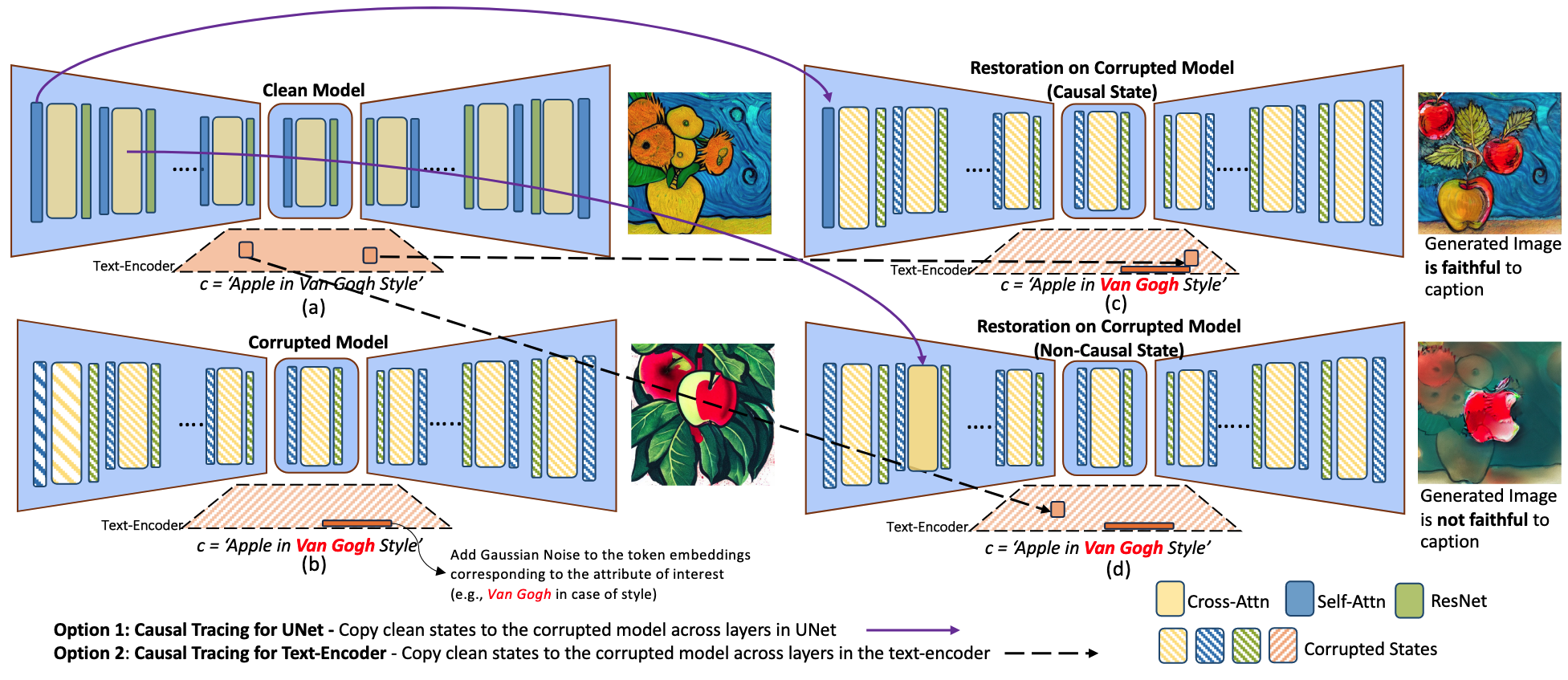
Clean Model에서 Causal State를 Corrupted Model로 옮겼더니 제대로 생성 됨
- Causal Mediation Analysis를 텍스트-이미지 생성 모델에 적용하여 지식의 위치 추적
- 원본 모델: 정상적으로 프롬프트에 응답하는 모델
- 손상된 모델: 관심 속성의 토큰 임베딩에 가우시안 노이즈를 추가한 모델
- 복원된 모델: 손상된 모델에 원본 모델의 특정 레이어 상태를 복사한 모델
- CLIP-Score를 사용하여 인과 상태 추출 및 임계값 선택을 위한 소규모 사용자 연구 수행
- 복원된 모델과 손상된 모델간의 CLIP Score 차이를 지표로 이용 → 차이가 클 수록 원래 프롬프트를 잘 나타낸 것이므로 해당 레이어/토큰은 Causal State를 가졌다고 볼 수 있음
- 객체, 스타일, 색상, 행동 등 네 가지 다른 시각적 속성에 대한 분석 진행
- UNet 인과 추적: UNet의 다양한 레이어에서 지식 위치 분석 → UNet은 지식이 여러 레이어에 고루 분포되어 있음
- 텍스트 인코더 인과 추적: 텍스트 인코더의 다양한 레이어에서 지식 위치 분석 → Text Encoder는 첫 번째 레이어의 Subject Token에 집중됨
DIFF-QUICKFIX
- 텍스트 인코더에서 인과 상태가 하나만 존재한다는 관찰을 활용하여 모델 편집 방법 개발
- 텍스트 인코더의 첫 번째 Self-Attention 레이어의
행렬에 대한 Closed-Form 업데이트를 통해 모델 편집 - Wout 행렬 최적화를 위한 수식:
- Van Gogh제거의 경우
가 Van Gogh의 전 값, 가 Painting과 같은 대체 텍스트의 기존 Pretrained Model의 이후의 값
- Van Gogh제거의 경우
- 이에 대한 Closed-Form 해:
- 학습 없이 위 계산으로 구할 수 있다는 의미
Method 검증
UNet에서의 지식 위치 발견
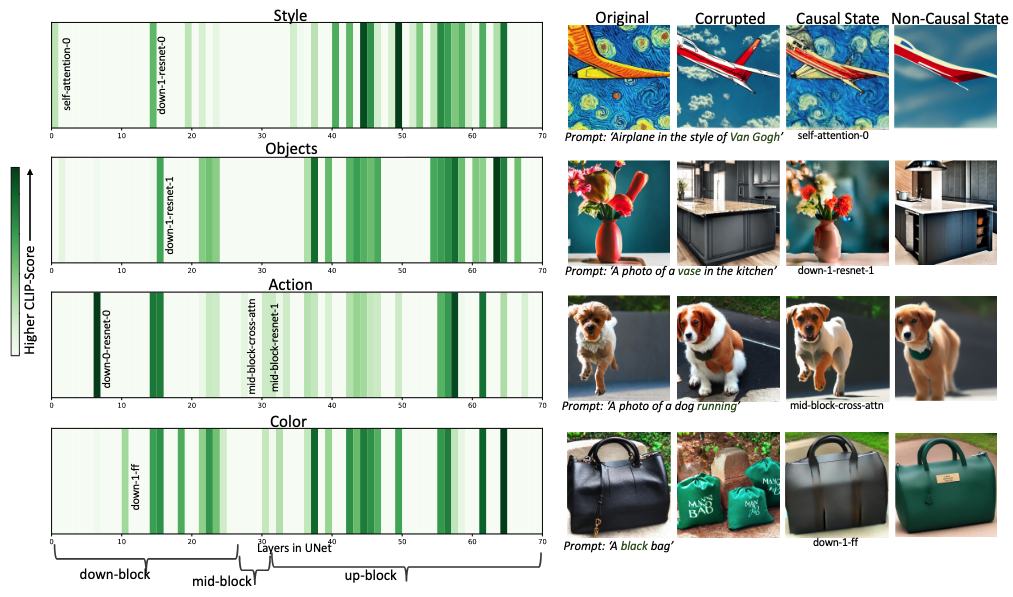
- UNet에서는 지식이 여러 컴포넌트에 분산되어 있으며, 속성별로 다른 분포 패턴을 보임
- 스타일: 첫 번째 Self-Attention 레이어가 스타일 관련 지식을 저장하지만, 다른 속성에는 인과적으로 중요하지 않음
- 행동: 미드블록 Cross-Attention 레이어가 인과적으로 중요하지만, 다른 속성에는 중요하지 않음
- Up-Block에 인과 상태가 더 많이 분포 → UNet 깊은 층에서 시각적 속성에 대한 지식이 더 많이 저장됨
- 예상과 달리 Cross-Attention 레이어가 항상 인과적으로 중요한 상태가 아님, ResNet 블록과 Self-Attention 블록에도 상당한 양의 지식이 저장됨 → 텍스트-이미지 모델에서의 지식 분포가 기존 가설보다 복잡함
텍스트 인코더에서의 지식 위치 발견
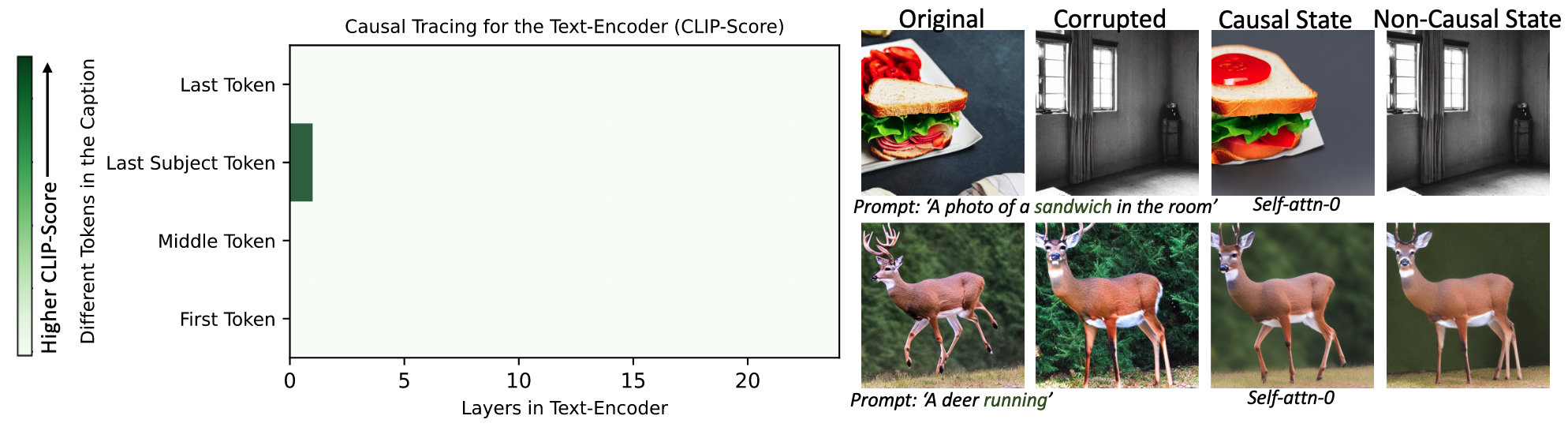
- 텍스트 인코더에서는 모든 속성에 대해 지식이 강하게 국소화됨
- 마지막 주제 토큰의 첫 번째 Self-Attention 레이어에 지식이 집중됨 → UNet과 달리 텍스트 인코더에서는 하나의 핵심 인과 상태 존재
- 이는 GPT와 같은 언어 모델에서 중간 MLP 레이어에 사실적 지식이 저장된다는 이전 발견과 대조적 → 모델 아키텍처별로 지식 저장 메커니즘이 다름을 시사
DIFF-QUICKFIX 평가
- 스타일 및 객체 제거: 기존 Fine-Tuning 방식과 비교하여 유사한 CLIP-Score 달성(약 0.22-0.23)하며 1초 미만의 편집 시간 → 1000배 빠른 속도로 효과적인 개념 편집 가능
- 오래된 지식 업데이트: "Trump가 대통령(예전 사실)"일 때 높은 CLIP-Score(0.28)를, "Biden이 대통령(현재 사실)"일 때 낮은 점수(0.22) 보임 → DIFF-QUICKFIX 적용 후 "Biden이 대통령" 점수는 증가(0.29)하고 "Trump가 대통령" 점수는 감소(0.23) → 대통령이 의미하는 바가 Biden과 더 가까워짐 → 모델이 가지고 있는 지식을 DIFF-QUICKFIX로도 개선할 수 있음
- 다중 개념 동시 편집: 최대 10개의 서로 다른 스타일과 객체를 동시에 제거하면서도 단일 개념 편집과 비슷한 CLIP-Score 유지 → 실용적인 다중 개념 편집 가능성 입증